Ferret Poop | A Complete Guide

Ferrets are fascinating pets, but their poop and litter box can be a topic of concern for owners. Understanding the intricacies of ferret waste, such as feces, is crucial for any ferret owner, as it provides valuable insights into their furry friend’s well-being.
We’ll explore the various factors that affect ferret feces, including diet and potential health issues. We’ll provide practical tips on how to monitor and maintain your ferret’s digestion and kibble stools.
By the end of this post, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of what constitutes normal and abnormal ferret poop – empowering you to ensure your pet stays happy and healthy.
Topics Covered In This Article
Poop Basics
Health Indicators
Ferret poop can indicate overall health. Changes in poop may signal underlying health issues. Regular monitoring of poop can help assess ferret’s health.
Keeping an eye on their poops is crucial. The characteristics of their feces serve as valuable indicators of their internal health. By regularly checking your furry friend’s feces, stools, or diarrhea, you can gain insights into potential digestive or gastrointestinal problems they might be facing.
Any alterations in the color, shape, or consistency of their stools could signify underlying health issues that require attention.
Monitoring your ferret’s feces also allows you to detect any irregularities early on and seek veterinary assistance promptly if necessary.
For instance, if you notice sudden changes in the frequency of bowel movements or a significant shift in the appearance of their stools, this could indicate an underlying disease that needs addressing.
Regularly observing your ferret’s feces enables you to establish what constitutes normal for them so that any deviations from this baseline become immediately apparent.
This familiarity with your pet’s regular poop patterns empowers you to identify potential health concerns at an early stage before they escalate into more serious issues.
Importance of Observation
Examining your ferret’s feces is not just about ensuring cleanliness; it plays a key role in maintaining their overall well-being too.
- It helps identify abnormalities: Regular inspection allows you to spot any unusual changes such as discolouration or irregular shapes.
- Anomalies in the color, shape, or consistency of stools can act as precursors to underlying gastrointestinal diseases.
- Prompt action: Being vigilant about examining your pet’s feces ensures timely intervention when necessary.
Understanding Normal Poop
Appearance
Normal ferret stools can vary in appearance depending on the ferret’s diet and overall health. The stools typically has a light tan to brown color, with a smooth, toothpaste-like consistency, and is tubular in shape.
However, exposure to air can cause it to dry out, leading to shrinkage and a change in colour to dark brown. Any unusual appearances in ferrets’ stools should be noted for veterinary consultation as they may indicate underlying health issues.
For example, if you notice that your ferret’s stools are unusually soft or watery, it could be a sign of diarrhea. On the other hand, firm and well-formed poops are indicative of good digestive health. Therefore, monitoring the texture of your ferret’s stools is crucial for assessing its overall well-being.
Texture
The normal ferret stools should have consistent texture which reflects their digestive health. Different textures of stools may indicate different conditions or issues within the gastrointestinal tract.
Therefore, it’s important to pay attention not only to the colour but also how firm or soft their stools are; any inconsistencies might require prompt vet consultation.
Ferrets’ diets play an essential role in determining their stool colour as well as potential changes due to illness within the gastrointestinal tract.
While normal ferret stools range from brown to dark brown in colour due to diet variations and hydration levels. Abnormal colors such as red or black may signal internal bleeding requiring immediate veterinary attention.
Abnormal Poop Signs
Black Tarry Stools
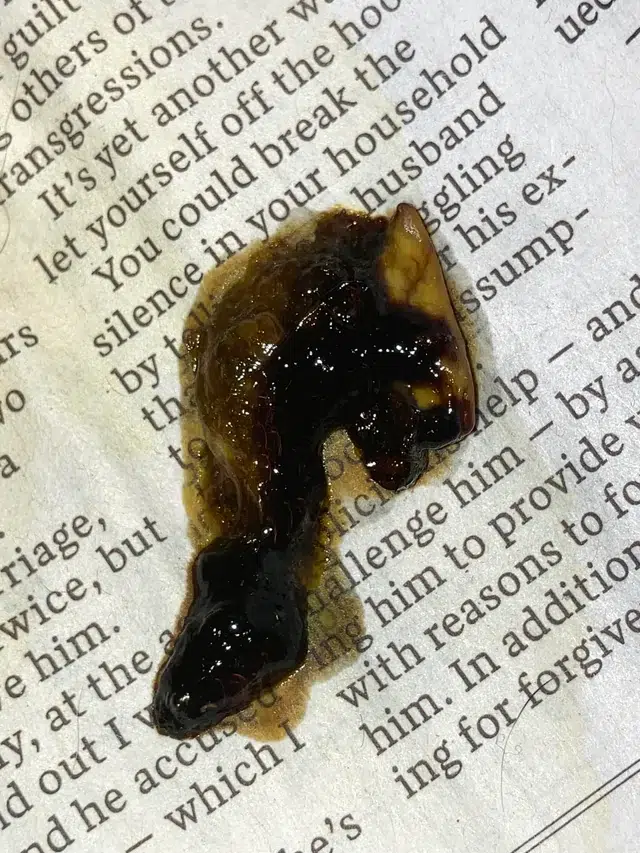
Black tarry stools in ferrets could signal bleeding in the upper digestive tract. This type of stool is a cause for concern and requires immediate veterinary evaluation. If you notice black tarry stools, it’s crucial to monitor your ferret for this type of stool as early detection is vital.
Bleeding in the upper digestive tract can be a serious issue, and prompt attention from a vet is essential. Keep an eye out for any changes in your ferret’s stools, as black tarry stools can indicate underlying health problems that need urgent medical intervention.
Yellow Poop Concerns
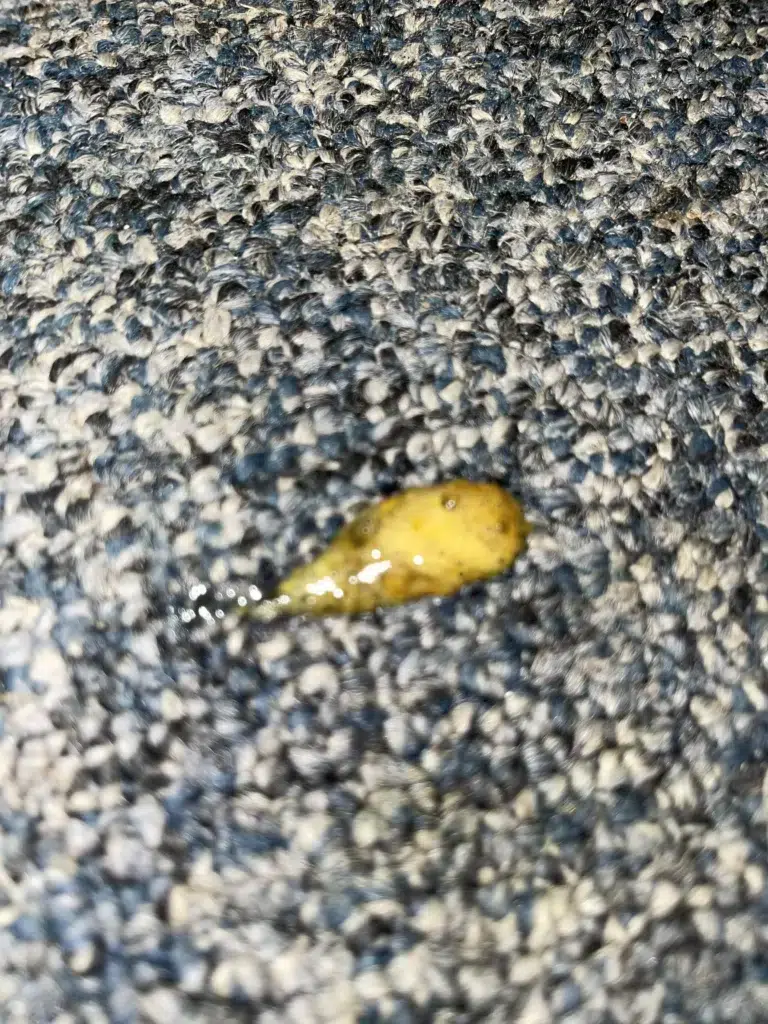

Yellow stools in ferrets may suggest liver or gallbladder issues. While dietary changes can also cause temporary yellowing of stools, persistent yellow poop should prompt a visit to the vet. Liver or gallbladder problems are significant health concerns that require professional assessment and potential treatment.
If you observe persistent yellow stools, it’s important not to delay seeking veterinary advice. The colour change may be indicative of an underlying condition requiring medical attention beyond just dietary adjustments.
Green Poop Mysteries
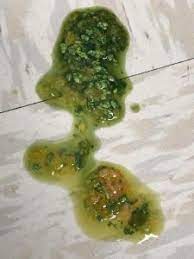
Green stools in ferrets might result from dietary changes or infections within their system. It could indicate rapid transit time through the intestines due to intestinal hypermotility – a condition where there is increased movement within the intestines leading to incomplete digestion of biliverdin resulting in green stools with bird-seed appearance.
When faced with persistent green poop or stools, it’s important to seek investigation by a vet as this may signify an underlying health issue needing professional diagnosis and care.
The colour variations observed in ferret stools can provide valuable insights into their health status; however, they do not always pinpoint specific anatomical regions affected by disease processes.
For instance, while green slime has been associated with certain diseases like ECE (green slime) in ferrets, it does not exclusively point towards them but rather indicates non-specific abnormalities necessitating further examination by veterinarians.
Ferret owners should remain vigilant about any deviations from normal stool appearances such as deep gray feces indicating severe anaemia or bile duct obstruction which though rare still warrants consideration when observed.
Remember that changes in ferret poops serve as critical indicators of their overall well-being and necessitate timely actions such as consulting veterinarians when unusual signs manifest.
Gastrointestinal Health
Diet Impact
A ferret’s poop is greatly influenced by its diet. For instance, a well-balanced diet results in healthy and well-formed poops. Try to provide your ferret with a diet that is high in protein, fats and low in carbohydrates, fiber and sugar. Conversely, sudden changes in the diet can lead to digestive disturbances, affecting the color and consistency of the ferret’s poop.
When a ferret experiences abrupt dietary changes, it can lead to irregularities in its poop. Such inconsistencies may include alterations in colour or texture. Therefore, it’s crucial for ferret owners to ensure that their pets have a consistent and appropriate diet to maintain healthy gastrointestinal function.
Disease Symptoms
Changes in a ferret’s poop can serve as early indicators of underlying health issues such as ECE (epizootic catarrhal enteritis) or gastritis. Monitoring these symptoms is essential for early intervention when necessary.
Ferrets suffering from certain diseases may exhibit noticeable changes in their stool patterns, including variations in colour or texture. For example, bright red blood or mucus content within the feces could be symptomatic of gastrointestinal ailments requiring immediate veterinary attention.
The context provided highlights various signs that indicate potential gastrointestinal problems such as dark and tarry stools resulting from gastric ulcers indicating severe hemorrhage. Watery feces with mucus content are indicative of colonic disease.
Illness Indicators
Mucus Presence
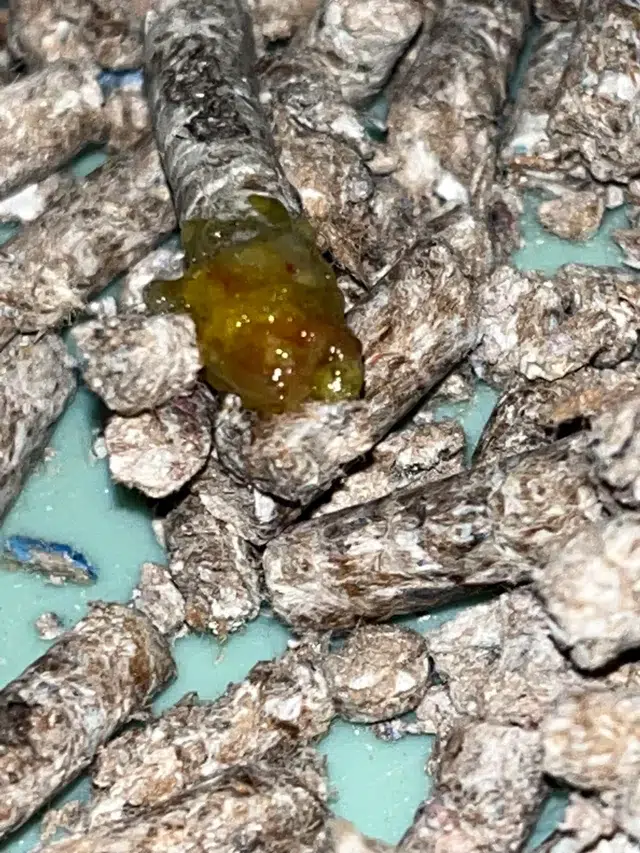

Mucus in ferret poop can indicate gastrointestinal irritation or infection. While a small amount of mucus is normal, excessive presence may signal an underlying issue. Regularly checking for mucus in your ferret’s stool can help detect potential problems early on. If you notice an abnormal increase in mucus, it’s crucial to seek veterinary advice promptly.
Ferrets with melena, characterized by the black and tarry appearance of feces due to the presence of digested blood, may also exhibit increased mucus in their poop.
This could be a sign of a serious underlying disease that requires immediate attention from a veterinarian. In such cases, diagnostic procedures like blood tests and imaging studies might be necessary to identify the root cause.
Regular monitoring for mucus is essential as it serves as an early indicator of possible gastrointestinal issues in ferrets. Addressing these concerns promptly can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment and recovery.
Blood Traces

The presence of blood in ferret poop is abnormal and demands urgent veterinary care. It could signify severe conditions such as ulcers or parasites affecting your pet’s digestive system. Regularly inspecting your ferret’s stool for any signs of blood traces is vital for early detection and timely intervention.
When discussing melena, which manifests as dark stools due to the ingestion or digestion of blood, it becomes imperative to highlight that this condition often goes hand-in-hand with noticeable amounts of blood present in the faeces.
Ferrets displaying symptoms related to melena should receive immediate medical attention from a qualified veterinarian who can conduct thorough examinations and recommend appropriate treatments based on accurate diagnoses.
Poop Consistency Issues
Runny Stools
Ferret poop consistency is a crucial indicator of their health. Runny stools in ferrets can be caused by dietary indiscretion or infections. These issues often lead to dehydration, which requires prompt management to prevent further complications. If your ferret experiences persistent runny stools, it’s essential to seek veterinary assessment for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Dehydration often accompanies runny stools, posing a significant risk to the ferret’s health. It’s important to monitor your pet for signs of dehydration such as lethargy, dry gums, and sunken eyes if they have runny stools.
Seedy Appearances
Another aspect of ferret poop consistency is its seedy appearances. When you notice seedy appearances in your ferret’s poop, it may indicate undigested food particles. While this isn’t always a cause for concern, excessive seed-like material could signify malabsorption issues that need attention. This can also be caused due to the ingestion of foods that might not be supported by the ferret digestive system such as fruits and vegetables or any non-plant based foods.
Monitoring the presence of seedy appearances in your ferret’s poop helps gauge their digestive efficiency over time. By observing any changes in this aspect of their stool consistency, you can identify potential issues early on and take appropriate action to maintain your pet’s health.
Pooping Patterns
Frequency Matters
Ferret poop, also known as feces, is an essential indicator of a ferret’s health. These small animals have a fast metabolism, leading them to pass stool frequently – typically around 8 to 10 times a day.
Monitoring their pooping frequency is crucial because it helps in identifying any changes in their bowel habits. Significant increases or decreases in the ferret poops should be noted and investigated promptly.
Keeping an eye on how often your ferret defecates can provide valuable insights into their overall well-being. For instance, if you notice that your ferret is suddenly pooping less frequently than usual, this could indicate an underlying health issue that needs attention.
On the other hand, if there’s a sudden increase in the frequency of ferret poop, it could also signal potential health concerns that require veterinary evaluation.
Hydration Effects
The hydration levels of ferrets play a significant role in determining the consistency and quality of their poop. Proper hydration is crucial for maintaining healthy stool formation. When ferrets are adequately hydrated, their ferret poop tends to be well-formed and easy to pass.
However, dehydration can lead to dry and hard stools, which not only cause discomfort for the ferret but may also indicate potential health issues.
As responsible pet owners, ensuring that our furry friends have access to clean water at all times is vital for preventing dehydration-related problems with their bowel movements.
By observing the consistency of your ferret’s poop, you can gauge whether they are getting enough fluids or if adjustments need to be made to ensure optimal hydration levels.
Non-Pooping Concerns
Constipation Causes
Constipation in ferrets can be caused by various factors such as dietary choices, dehydration, and blockages in their digestive system. It’s important to monitor the ferret’s pooping habits regularly to identify signs of constipation early on. If a ferret is showing signs of discomfort or not passing stool regularly, prompt intervention is necessary to alleviate constipation.
Diet plays a crucial role in preventing constipation in ferrets. Ensuring they have access to high-quality food that contains sufficient fibre can help prevent this issue. Providing ample water and hydration is essential for maintaining healthy bowel movements in these small animals.
Blockages, often caused by ingesting foreign objects, can also lead to constipation and require immediate veterinary attention.
Regular monitoring helps detect any changes in the ferret’s pooping patterns which might indicate an underlying problem like constipation. By observing their litter box habits daily, pet owners can notice if there are any irregularities or significant deviations from normal behaviour.
Remedies and Solutions
Dietary adjustments are often effective remedies for alleviating constipation issues. Introducing more animal-based foods into their diet can promote regular bowel movements and prevent future episodes of constipation.
However, it’s crucial for pet owners to seek veterinary guidance before administering any remedies or treatments for their ferret’s poop-related concerns. Consulting with a veterinarian ensures that the appropriate measures are taken based on the specific needs of each individual animal.
Proper treatment prescribed by a vet ensures an effective resolution of stool issues without causing further harm or complications for the ferret.
This may involve medication or other interventions tailored specifically to address the underlying cause of the constipation while prioritising the well-being and health of the animal.
Proper Poop Management
Disposal Hygiene
Ferret poop is an essential aspect of ferret owners’ responsibilities. Proper disposal of soiled bedding and litter is crucial for maintaining a clean and healthy environment for your ferret.
Regular cleaning reduces the risk of reinfection from contaminated areas, promoting a hygienic living space for your pet. By maintaining good hygiene practices, ferret owners contribute to their pet’s overall health.
Regular cleaning of the litter tray not only ensures a clean environment but also prevents the spread of diseases. For instance, disposing of soiled bedding promptly helps in preventing the transmission of parasites or bacteria that may be present in the feces.
As responsible ferret owners, it’s important to ensure that waste is disposed of properly to safeguard both your ferret’s health and yours.
Monitoring Health
Observing and monitoring healthy ferret poop aids in assessing your ferret’s overall health status. The consistency, colour, and frequency are key indicators that can provide valuable insights into your ferret’s well-being.
Any abnormalities detected during this monitoring process can prompt timely veterinary intervention, potentially averting any serious health issues.
Summary
Understanding your ferret’s poop is crucial for their overall health. From recognising normal poop to identifying signs of illness, you’ve gained valuable insights into their gastrointestinal well-being.
Remember, consistency matters, and any deviations from the norm could indicate underlying issues. Proper poop management is essential for keeping your ferret healthy and happy.
Now that you’re equipped with this knowledge, take proactive steps to monitor your ferret’s poop regularly. If you notice any abnormal signs or have concerns about their gastrointestinal health, don’t hesitate to seek professional veterinary advice. Your ferret relies on you to be their advocate for good health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Normal ferret poop should be dark brown, well-formed, and cylindrical in shape. It shouldn’t be too hard or too soft. Think of it like a firm chocolate-covered raisin! If you notice any significant changes in colour, consistency, or frequency, it’s best to consult a vet.
Ferrets typically poop 8-10 times a day. They’re quite the little pooping machines! Keep an eye on their litter box habits to ensure they’re maintaining their regular pooping pattern. Any sudden increase or decrease in frequency could indicate an underlying issue.
Abnormal signs include extremely smelly or runny stools, blood in the stool, unusually light or pale colouring, and mucus-covered faeces. These can all point towards gastrointestinal issues that require attention from a vet. It’s important not to ignore these warning signs!
Proper management involves keeping their living area clean by scooping out soiled litter daily and ensuring they have access to fresh water at all times. Feeding them a balanced diet rich in protein will contribute to healthy digestion and better quality poops.
If your furry friend hasn’t produced any stool for more than 24 hours or is showing signs of discomfort while trying to defecate (straining), it’s time for a trip to the vet. A lack of bowel movements could indicate an obstruction that needs immediate attention.
Last Updated on 19 January 2024
Waman Nuka is a seasoned wordsmith and a passionate animal enthusiast with decades of experience in the world of animal care. With a deep love for all creatures great and small, Waman’s journey in the realm of animals started as a young boy exploring the lush forests surrounding his childhood home.


